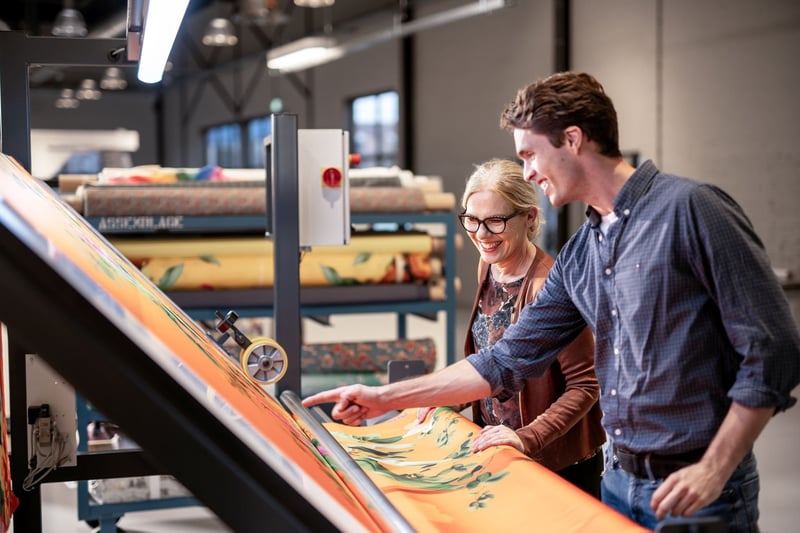
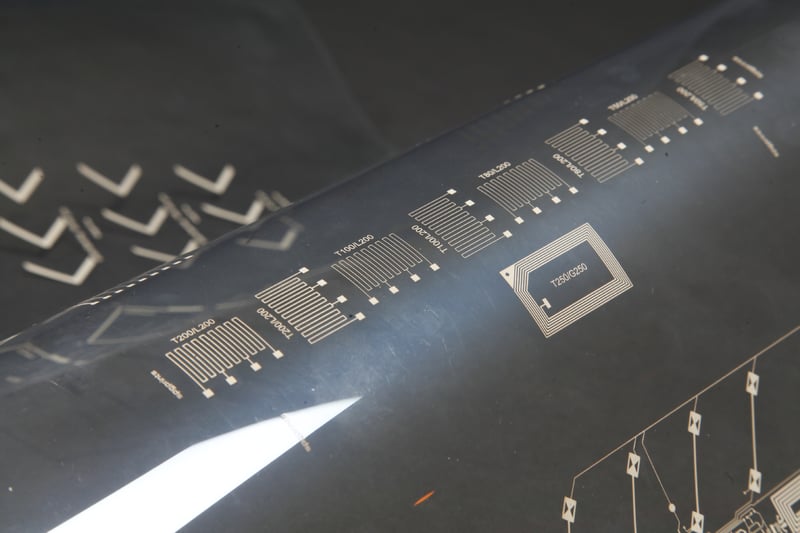
As more and more electronic devices are (partly) produced through Printed Electronics, flexibility becomes increasingly important. Flexible Electronics are a well-known phenomenon in the printing world, but which manufacturing method creates the best results for your printing line? And how do you take the environment into account?
Flexibility in Flexible Electronics
Flexible refers to the substrate which can be a broad range of film material, like PET and PI. But also, paper is becoming more and more popular, due to the environmental advantages. There are many different qualities available with all kinds of possible specifications suitable for various applications. These can be supplied on a roll or in sheets.
Due to the many advantages that this flexibility offers, the possible applications are countless. Not only does flexibility allow us to produce small components in large numbers, but it also saves weight and costs. Everything can be made smaller, lighter and more compact by flexible PCB fabrication. This is very important for applications like laptops and mobile phones. Many of these devices have become much smaller over the years.
Cars are executed with more and more electronic devices as well. There are more safety devices around the vehicle integrated. Inside the car, there’s a massive change to electronic control devices in combination with in-mold panels.
Other industries where Flexible Electronics are often used are the healthcare industry and the energy sector, such as solar panels and printed batteries.
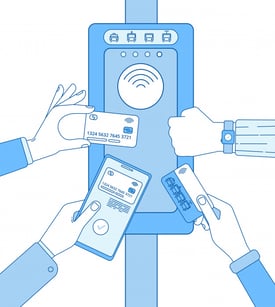
One of the biggest applications of Flexible Electronics are products in which RFID techniques are applied. RFID stands for Radio Frequency Identification; objects can be identified by using radio waves. Applications are library books, traceability in the supply chain, bank cards and livestock. All can be equipped with RFID technology.
A Sustainable Solution for printed Flexible Circuit Boards
The downside is that a lot of these applications are produced by subtractive production methods like etching and laser ablation. In the etching process, redundant material is removed to produce a final shape and product. This production method is harmful to the environment, as a lot of residual waste remains.
Fortunately, RFID applications are increasingly printed on paper and/or foil, which makes it much easier to recycle. The printing can be done with Rotary Screen Printing, making PCB fabrication more sustainable. This is an important development, now that Flexible Electronics are being used more and more in a wide range of applications.
Rotary Screen Printing for Flexible Electronics
As the name suggests, Rotary Screen Printing is a rotary process. It is a continuous printing process; you can print many of the same applications in succession. This is a great advantage for products that are mass-produced. An important condition is that the substrate must be on a roll base.
Not only is Rotary Screen Printing a very sustainable way of printing Flexible Electronics ideally suited for mass production, but the accuracy that can be achieved with Rotary meets the current needs. (up to 80μm). If you are currently using flatbed screen printing or another printing method, and Rotary Screen Printing would be suitable for your company, it is important to know that the conversion from a flatbed screen application towards Rotary Screen Printing can normally be executed easily.
Benefits and drawbacks of Rotary Screen Printing
The integration of Rotary Screen Printing into your production process can be done easily because the process remains largely the same. The main thing you want to achieve is that the inks are applied to your substrate in exactly the right amount and thickness at the right place. This requires accuracy, but the current (and future) market also demands high volumes and fast production times. With the Rotary Screen Printing technique, you can print the same product many times in a row very accurately.
Although the sustainability aspect and the possibilities for mass production are huge advantages, Rotary Screen Printing also has drawbacks. For example, the speed of Rotary Screen Printing can also be seen as a disadvantage. After all, you need to be sure that what you print is flawless. If this is not the case, you will print the same error again and again as soon as the print line is running. This can lead to a lot of waste, which counteracts sustainability. When printing complex products this can be solved by monitoring with cameras. Running tests beforehand is also a solution, but this is time-consuming.
Printing in register is also important when producing flexible PCBs. It might not be able to reach the high accuracy of some flatbed printers, but it is still more than sufficient for most applications. Always check whether your application is feasible with Rotary Screen Printing beforehand.
Important to notice is that the biggest advantages of Rotary Screen Printing emerge as soon as larger print runs are involved. When the volumes get higher, the price per piece can be reduced considerably. This is why Rotary Screen Printing and mass production go hand in hand.
The best solution for your specific printing line
What is the best type of printing process for your business and the applications you produce? Talking to an expert about your printing process and how to optimize your print line might help in making the right decision. Contact us here, our Printed Electronics specialists are always happy to help!
You can also download our free-to-download Comparison Sheet, in which we compare two common solutions: Flatbed and Rotary Screen Printing. What are the big differences and which one suits your manufacturing process best? Download your copy here:

%20%7C%20Challenge%20Ben%20page.jpeg?width=1600&name=Ben%20RSI%20(re-sized%20for%20loading)%20%7C%20Challenge%20Ben%20page.jpeg)