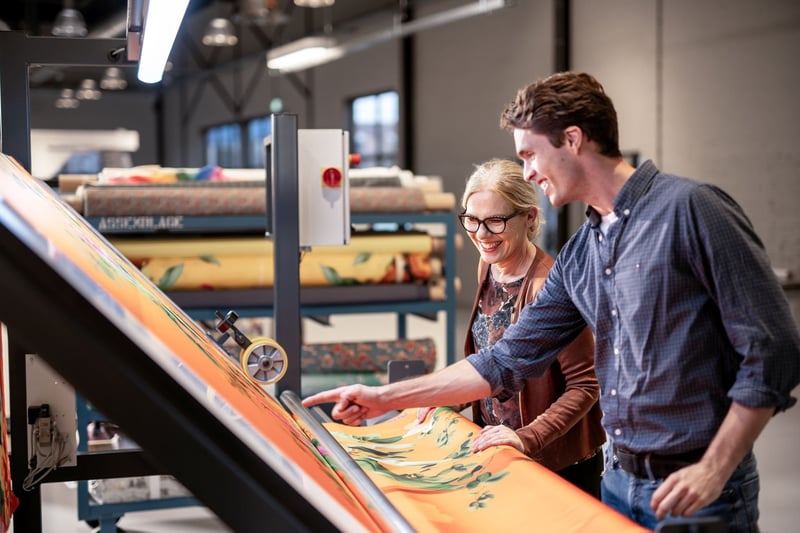
Despite its widespread use, flatbed screen printing faces several inherent limitations that significantly impact its effectiveness and efficiency for large-scale industrial production. One of the primary drawbacks is the process's relatively slow nature, as it is constrained by the necessity to print each layer sequentially. This step-by-step approach not only elongates production timelines but can also result in bottlenecks, especially when high-volume output is required. Additionally, the need for frequent screen changes and setup adjustments results in considerable downtime, which can severely disrupt workflow and reduce overall production efficiency.
This downtime is particularly problematic in high-demand environments where every minute of production counts. Furthermore, the physical dimensions of the flat screen itself impose restrictions on the size of the printed electronics that can be produced, inherently limiting the method's suitability for applications that demand larger or continuous prints. These size constraints can be a significant barrier when attempting to meet the needs of industries that require expansive and uninterrupted print patterns. Consequently, while flatbed screen printing may serve well for smaller, less demanding projects, its limitations make it less ideal for modern industrial applications that prioritize speed, efficiency, and scalability.
Exploring Rotary Screen Printing
Rotary screen printing represents a significant advancement over flatbed technology, particularly for industrial-scale printed electronics production. This method employs a cylindrical screen that rotates continuously, allowing for a more streamlined and efficient printing process. The rotary approach excels in high-speed production environments, delivering consistent, high-quality outputs with minimal downtime.
One of the standout features of rotary screen printing is its ability to handle long runs and repeat orders efficiently. The continuous nature of the process reduces the risk of blockages and downtime, ensuring a smooth production flow. Additionally, rotary screens can be stripped and reused multiple times, enhancing sustainability and reducing operational costs.
Comparative Analysis: Speed and Efficiency
When comparing flatbed and rotary screen printing, speed and efficiency are critical factors. Flatbed printing is inherently slower due to its sequential nature, making it less suitable for high-volume production. Setup times and the need for frequent screen changes further exacerbate downtime, impacting overall productivity.
In contrast, rotary screen printing offers significant advantages in speed and efficiency. The continuous rotation of the cylindrical screen allows for faster printing cycles, reducing the time required to produce each unit. This method also minimizes downtime, as screens can be changed quickly and the risk of blockages is substantially lower. For manufacturers looking to scale up production, rotary screen printing provides a clear edge in operational efficiency.
Quality and Consistency in High-Volume Production
Quality and consistency are paramount in the production of printed electronics, where even minor deviations can impact functionality. Flatbed screen printing, while cost-effective, often struggles with maintaining consistent quality across large production runs. The manual nature of the process and the limitations of the flat screen can result in variations that compromise the final product.
Rotary screen printing, on the other hand, excels in delivering high-quality, consistent results. The precision of the cylindrical screen ensures that each print meets exacting standards, reducing the risk of defects. This consistency is crucial for applications requiring intricate electronic circuits and components, where reliability is non-negotiable. For high-volume production, rotary screen printing offers a level of quality assurance that flatbed methods cannot match.
Scalability and Flexibility for Future Applications
Scalability is a significant consideration for manufacturers in the printed electronics industry. While flatbed screen printing offers flexibility for small-scale and prototype production, it falls short when transitioning to industrial-scale operations. The limitations in speed, size, and consistency make it challenging to scale up without compromising quality and efficiency.
Rotary screen printing provides a scalable solution that can adapt to varying production needs. Its ability to handle long, continuous prints makes it ideal for large-scale applications, from flexible solar panels to RFID tags. The technology's inherent flexibility also supports future innovations, allowing manufacturers to incorporate new materials and designs as the industry evolves. Investing in rotary screen printing ensures that manufacturers are well-positioned to meet growing demand and capitalize on emerging opportunities.
Making the Right Investment for Your Business
Choosing between flatbed and rotary screen printing is a critical decision for manufacturers looking to scale up their printed electronics production. While flatbed printing offers a low-cost entry point, its limitations in speed, quality, and scalability can hinder long-term growth. Rotary screen printing, with its superior efficiency, consistent quality, and scalability, represents a more substantial initial investment but delivers significant long-term benefits.
Investing in rotary screen printing technology early in the development cycle can streamline the transition to industrial-scale production, reducing time to market and enhancing competitive advantage. Manufacturers can integrate the technology into existing processes, optimize formulations, and calibrate equipment to maximize efficiency and output quality.
In conclusion, while both flatbed and rotary screen printing have their merits, the choice ultimately depends on the scale and scope of your production needs. For businesses aiming to lead in the dynamic and rapidly growing field of printed electronics, rotary screen printing offers a robust, future-proof solution that ensures long-term success and innovation.