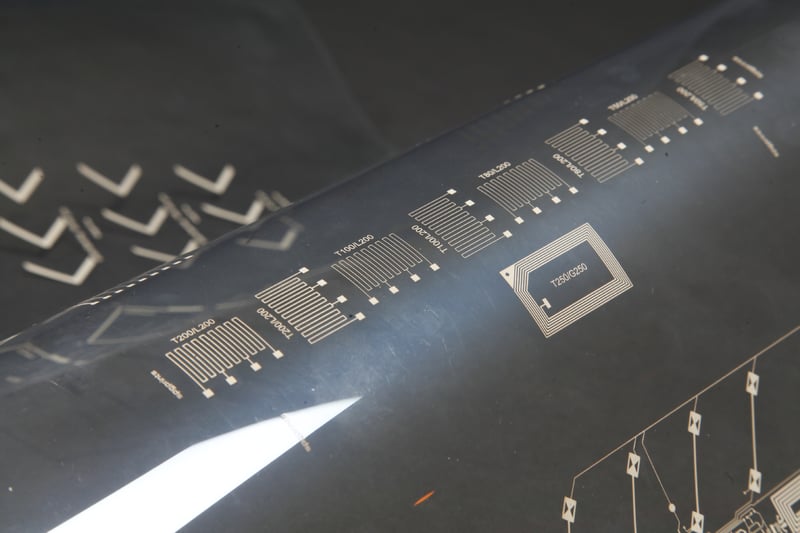
Flatbed screen printing is a well-known technique for Industrial Printing (like Printed Electronics and Label Printing). A somewhat less familiar solution for these applications is the rotary screen printing process.
Although both techniques work differently, they have many similarities. However, they also both have their unique advantages. For example, seamless printing is not possible with flatbed screen printing, while it can be done in a rotary screen printing process.
But what is the best solution for your manufacturing process? What are the most relevant differences for your printing process and which technique can help you to improve your Industrial Printing line best?
5 points of comparison
In order to make a comparison as complete as possible, our Industrial Printing and Printed Electronics experts have prepared a free-to-download Comparison Sheet. This sheet covers all relevant factors if you’re selecting a screen printing technique for your Industrial Printing line.
/Special%20sreens%20-%20LEX%20Industrial%20(Albatros)_LEX%20Industrial%203_laser%20engraver_156.jpg?width=2048&name=Special%20sreens%20-%20LEX%20Industrial%20(Albatros)_LEX%20Industrial%203_laser%20engraver_156.jpg)
In this blog, we will take a closer look at 5 points covered in this Comparison Sheet:
- Printing Pace & Continuity
- Printing High Volumes & Reproducibility
- Blockages of Printing Holes
- Lifespan of Screens
- Integrating for Various Purposes
1. Printing Pace & Continuity
The first important difference is pace, directly influenced by continuity. Flatbed screen printing is practically done in 2 strokes. First, the ink is spread across the screen so that the holes in the mesh can fill up with ink. This is called prefilling. In the second stroke, the squeegee presses the ink through the screen onto the substrate. This means the squeegee will have to go back and forth for a single print image.
In rotary screen printing, these same steps are combined in a continuous process. Due to the ink roll that is in front of the squeegee blade, the mesh is already pre-filled without the need for an extra stroke. The squeegee has the same function here: it pushes the ink through the screen onto the substrate. However, it does not need its own stroke but is part of the continuous process.
To put it simply, one printed meter in flatbed screen printing requires one meter to prefill and one meter to print, whereas in rotary screen printing this takes just one meter. This results in a lower actual squeegee speed, with benefits for ink rheology.
The opposite is also true: flatbed screen printing often uses a higher squeegee speed to cover larger runs. However, if ink moves quickly, the viscosity might become higher. Because of this, the printing result is not constant. Rotary screen printing can use lower squeegee speeds, but achieve the same or even faster output, with a more constant printing result.
2. Printing High Volumes & Reproducibility
For some applications - such as printed circuit boards - applications are required to be mass-produced. For this kind of mass production, reproducibility and high-volume printing are of great importance.
These two factors are perhaps the most important selling points of rotary screen printing for Industrial Printing and Printed Electronics. As the name suggests, rotary screen printing is a rotary process that can run longer than other screen printing techniques. This ensures that the print line can continuously reproduce products and higher volumes are possible.
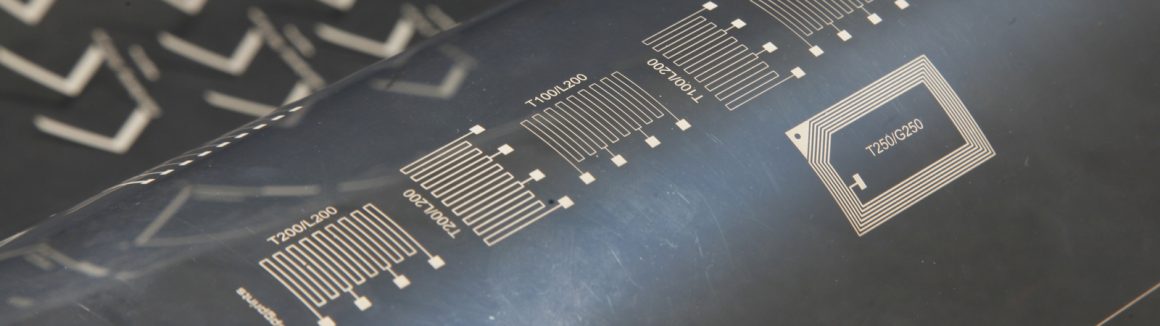
If your application benefits from high volumes and reproducibility of parts, a rotary screen printing process is almost always the most suitable solution.
3. Blockages of Printing Holes
For screen printing techniques, downtime and clogging of holes are the main dealbreakers. Clogged holes can influence the printing result, but can also cause (permanent) damage to machines or screens. This increases the - often unforeseen - costs even more.
Because the rotary screen printing process is a continuous process, including pre-filling, the printing result is much more consistent than other screen printing techniques. This is because there is no accumulation of ink on the sides of the machine. In flatbed screen printing, ink often sticks to the edges and dries there. This then ends up on the screen where it causes lumps, causing the holes to clog up.
As mentioned, this often harms the printing result. Therefore, when using flatbed screen printing, be aware to check frequently whether ink has accumulated unexpectedly. This might be an extra process step, but it can cause a lot of extra costs in the end.
4. Lifespan of Screens
Another aspect that can save costs in the long run, is the lifetime of tools. A frequently mentioned advantage of rotary screen printing is that the lifespan of screens is relatively high. Although the equipment investment for a rotary screen printing process is higher, less downtime and lower start-up costs result in a much higher lifespan of screens and thus lower costs in the long run.
Logically, a higher lifespan means that screens don’t need to be replaced as often. This reduces machine downtime, which in turn saves costs in the long run. Therefore, lifespan is a very important factor when selecting a screen printing technique for your Industrial Printing line.
5. Integrating for Various Purposes
Finally, integration with your existing print line is an important issue for many companies. Although rotary screen printing is ideally suited to high-volume printing, as mentioned in point 2, it can also be implemented for other purposes. The implementation of rotary screen printing is fairly easy when compared to flatbed screen printing.

You can also use the system to print short runs, which means you can carefully try out what suits your printing process best during the integration process. Because low speeds are also possible, rotary screen printing is very convenient for research and testing.
To try this out without any large investments, SPGPrints offers rental units to our customers. Using this service, you can test a rental unit within your manufacturing process, before buying a unit.
Comparing Screen Printing Techniques for Industrial Printing
In the previous chapters, we covered the most important differences between flatbed screen printing and the rotary screen printing process. But what is the best type of printing process for your business and the applications you produce?
Our experts created a free-to-download comparison sheet that compares the main advantages and challenges of screen printing techniques. With this sheet, you’ll always have the most important considerations at hand. Download your copy here:
Would you rather talk to an expert about your printing process and how to optimize your print line? Contact us here or request a proof of concept for your specific application!
/Special%20sreens%20-%20LEX%20Industrial%20(Albatros)_LEX%20Industrial%203_laser%20engraver_156.jpg?width=760&name=Special%20sreens%20-%20LEX%20Industrial%20(Albatros)_LEX%20Industrial%203_laser%20engraver_156.jpg)