Approximately half of all printed textile volume in the world is printed with pigment printing. Almost all of this pigment printing is done conventionally, with rotary screen printing. Digital pigment printing is still very rare. Why is that?
Pigment printing: advantages and disadvantages
Pigment printing is the cheapest way of rotary screen printing and it is possible on all types of fabric. These are two of its biggest advantages. Another big advantage is about sustainability: you don't have to steam and wash pigment printed fabric. It only has to be baked at a high temperature to stick. This is a simple process, which also makes pigment printing one of the easiest forms of printing. In short, the advantages of rotary pigment printing are:
- Cheap
- Flexible on fabrics
- Sustainable
- Easy-to-use
However, there are also some drawbacks to pigment printing. The so-called "hand of the fabric" is one of its weaknesses. The fabric feels rough and kind of harsh. Therefore, a fine fashion fabric normally will never be printed with pigment. The hand becomes slightly better after washing, but then pigment also loses some color. A second disadvantage is the rub fastness: by rubbing you can remove the particles from the sticking layer and lose your color. Thirdly, pigment printing is known for its lack of brilliant colors. This disadvantage is most noticeable when printing in black. Therefore, disadvantages of pigment printing are:
- rough hand
- low rub fastness
- not very brilliant colors
Digital Pigment Printing
Since pigment paste is by far the cheapest and easiest to print conventionally, understandably many printing companies ask whether it is also possible in digital textile printing. If it is the cheapest option in rotary screen printing, this will also be the case with digital printing, right?
Because of these questions, SPGPrints has been trying to find the best pigment solutions for digital since the mid 1990s. However, what makes pigment so simple and cheap in rotary screen printing, is a lot more difficult in digital. There are 3 main reasons for this:
- Necessity for a binder
- Particle size
- Stickiness
1. Necessity for a binder
Pigment paste contains a chemical binding solution to stick the pigment particles on the cloth. That binder has a relatively high viscosity and therefore it cannot be jetted through an inkjet head. This means you need to get the binder on the cloth in a different way.
The most common way to do this, is to pre-treat the binder on the cloth, let it dry and then spray the pigments in water-based ink on the cloth. If you bake it afterwards, the particles will still stick to the pre-applied binder, but with this solution you have added an extra (pre-) process step to your production. This means extra time, extra energy and a relatively expensive extra step (mainly because of the drying). One of the great advantages of pigment printing - the fast and easy process - is now lost.
2. Particle size
The second challenge of digital pigment printing is caused by the particle size of the pigments. Other ink types, such as reactive inks, involve dyes dissolved in water. But pigments are particles that do not dissolve and these particles are relatively large. So jetting them through a nozzle with only a few micrometers diameters is a challenge.
3. Stickiness
One of the big advantages of pigment printing was the fact that you can print anything with pigment ink because those particles stick to everything. However, if you combine the previously mentioned disadvantages with the fact that the particles indeed stick to everything, we have a problem with inkjet heads.
After all, this means the particles also stick to each other and become even bigger, as a result, the heads quickly become clogged. This may be prevented by cleaning the heads very regularly, but it is questionable if clogging can be completely avoided. Besides that, the extra time this takes means that once again a big advantage of pigment printing is nullified.
In the past, when the inkjet technology was so slow that one could print only a limited amount of square meters per hour, cleaning the printing heads regularly was acceptable. However, modern printing machines often print a few hundred or even thousands of meters an hour. With these numbers, it is prohibitive to print with pigment inks, as you don’t want to stop continuously to clean the printing heads.
Are Nano-pigments the solution?
A much suggested solution are nano-pigments: a technique in which the pigment particles are drastically reduced in size. The problem of clogging is reduced significantly with these miniscule particles, but the disadvantage is that these nano-pigments are relatively expensive to make. In addition, the pigment particles become so small that they lose most of their tinting strength in this way. This makes the colors even less brilliant than the conventional variants described above.
Admittedly, the tinting strength can be strengthened by putting more ink on a square meter but this makes this already expensive solution even more expensive. Besides that, there is a limit to it: as a comparison: putting 5 layers of grey paint on your wall does not make your wall black.
By solving one problem - the clogging of printing heads - other properties of pigment printing are worsened. Firstly, it makes the colors even less brilliant; secondly, it makes pigment printing for digital printers even more expensive.
The Digital Pigment Printing demand
As mentioned earlier, almost half of all rotary screen printing is printed with pigment printing. This is a great contrast to digital, where only 4% of all digital meters are printed with pigment printing. In 2017, this was just 3% (Fig. 1). However, the demand for digital pigment solutions is growing rapidly. Despite the disadvantages of digital pigment printing, many companies suggest that they have a suitable pigment solution for digital printers. In practice, however, these solutions often disappoint.
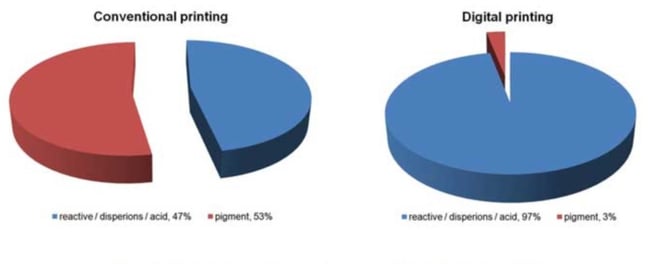 Fig 1. Worldwide textile printing market (Source: R. Wills, Digital Textile, 5/2017)
Fig 1. Worldwide textile printing market (Source: R. Wills, Digital Textile, 5/2017)
In the past, the demand for digital pigment printing was mainly held back by technical limitations, as described above. Most of these are nowadays significantly improved, but there are a few disadvantages compared to for instance reactive digital printing that remain: the low color strength, the relatively high ink consumption and the expensive inks. Nevertheless, the popularity of pigment solutions can be well explained. After all, steaming and washing with pigment printing is not necessary, which makes it a sustainable, more environmentally friendly alternative. This sustainability advantage helps in accepting the downsides.
For the time being, digital pigment printing is mainly used in applications in which bright colors are not necessary, such as bedding. In these kinds of markets, digital pigment printing is likely to advance faster and may one day even become the standard.
New developments and the future of digital pigment printing
In short, although pigment printing in rotary screen printing is one of the cheapest and easiest ways to print, almost all the advantages of conventional pigment printing are not valid for digital pigment textile printing. The costs are higher and the process of pigment printing takes more time.
There is one drawback of pigment printing - the hand which makes the cloth feel rough - which is clearly improved in digital pigment printing. Due to the small pigment particles, a cloth printed with digital pigment printing feels very similar to digitally printed designs with for instance reactives.
In the future, we want digital pigment printing to be as simple and cheap as its conventional counterpart. The expectation is that this will be possible in the future and that inventions will be made that will lead to more applications. Of course SPGPrints is actively involved in these developments and will be working continuously on new techniques. This way we will eventually bring a digital pigment technique that really works. However, for the time being digital pigment printing can’t match the advantages of rotary screen pigment printing, nor from digital reactive printing.
Would you like to learn more about the different ink forms and which type of ink can contribute to the improvements of your digital printing process? Our Selection Guide for Digital Inks can help you. Download it for free here: